Climate-Friendly Future with Sustainable Aviation Fuel
Ready for Departure: The Journey Towards a Climate-Friendly Future with Sustainable Aviation Fuel
The use of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) is on the rise, but what is it exactly?
Sustainable Aviation Fuel: Safe, Reliable, Low Carbon
SAF is a biofuel currently used in commercial aviation that has similar properties to conventional jet fuel but has a much smaller carbon footprint, reducing CO2 emissions by up to 80%.
100%
Made from 100% renewable raw materials and compatible with existing aircraft engines and airport fuel infrastructure
80%
Reduces GHG emissions by up to 80% over the fuel’s life cycle, compared to traditional fossil jet fuel
The Origins and Processes Behind SAF
SAF can be produced from a number of sources (feedstock) including waste oil and fats, green and municipal waste and non-food crops.
Some typical feedstocks used are cooking oil and other non-palm waste oils from animals or plants; solid waste from homes and businesses, such as packaging, paper, textiles, and food scraps that would otherwise go to landfill or incineration. Other potential sources include forestry waste, such as waste wood, and energy crops, including fast growing plants and algae.
In addition to these, SAF can also be produced synthetically through an innovative process that captures carbon directly from the air. This method, known as Direct Air Capture (DAC) technology – that removes carbon dioxide directly out of the atmosphere and converts it into fuel.
This not only helps decarbonise aviation and reduce the overall carbon footprint but also provides a sustainable way to recycle CO2, making it a crucial component in the fight against climate change.
Is SAF Really Low Carbon Solution?
Yes, and there’s more to it. While fossil fuels add to the overall level of CO2 by releasing carbon that has been stored underground for millions of years, SAF can have a much lower or a net-negative GHG footprint.
This is because some SAF production methods recycle CO2 that was absorbed by the biomass during its growth.
SAFs are considered sustainable because they:
- Captures carbon directly from the air.
- Do not compete with food crops.
- Require minimal additional resources like water or land clearing.
- Avoid contributing to environmental issues such as deforestation, soil degradation, or biodiversity loss.
In essence, by recycling CO2, SAF presents a significantly more sustainable and environmentally friendly option compared to standard fossil fuels.
Why is SAF important?
Jet fuel operates on high energy density that has enabled commercial flights. As of now, there are no other viable alternatives for transporting groups of people quickly over very long distances, making aviation heavily reliant on this fuel source.
For instance, a round trip between London and San Francisco has a carbon footprint per economy ticket of nearly 1 tonne of CO2e. With the aviation industry expected to double to over 8 billion passengers by 2050, it is essential that we act to reduce aviation’s carbon emissions and SAF is one way.
What Is the Contribution of SAF?
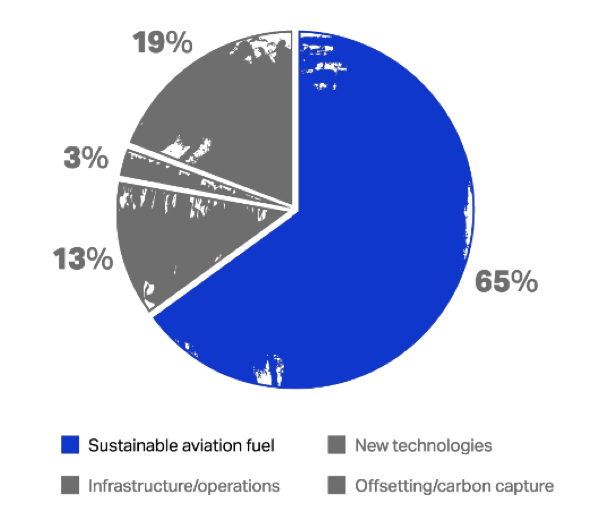
Figure 1: IATA – Net Zero 2050: Sustainable aviation fuels fact sheet
According to The International Air Transport Association (IATA), which represents some 320 airlines or 83% of total air traffic, Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) could contribute around 65% of the reduction in emissions needed by aviation to reach net zero CO2 emissions by 2050.
So Why Aren’t More Airlines Using SAF?
At the moment, production of SAF is limited due to its higher cost, which prevents wider uptake. Increasing demand in the short term will lead to more production and is expected to lower costs in the future.
Accelerating the Growth of SAF: Scaling Up Production and Current Availability
Achieving widespread awareness and acknowledgment of the potency of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is the initial step toward its acceleration. This entails active involvement at individual, corporate, and governmental levels.
On an individual level, passengers and corporate clients can reduce the emissions of their flights by funding the use of SAF through their ticket purchases. This positive initiative, offered by airlines, allows individuals to contribute directly to sustainability efforts.
On industry level, there is a strong commitment to reduce carbon emissions. As of February 27th, 2023, 96 airports worldwide are distributing sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), with 63 of them receiving regular supplies. This marks a significant increase from ten years ago when only one airport was capable of distributing SAF.
According to Bloomberg New Energy Finance (NEF), nearly 30 major global airlines have set targets to adopt SAF, aiming for 10% of fuel consumption by 2030,. More airports are also ensuring that carriers have access to SAF, further supporting this commitment.
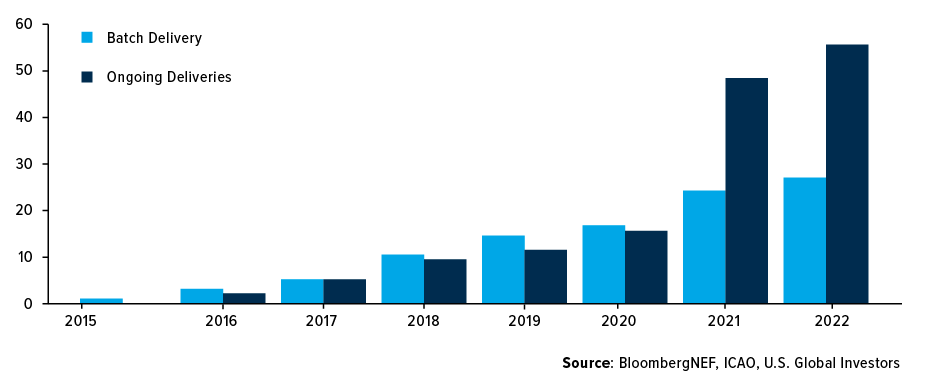
Figure 2: Number of airports distributing sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) from 2014 to 2023, by delivery type
However, to truly accelerate the growth of SAF, government intervention and subsidies are also required. Increasing production necessitates long-term policy certainty to reduce investment risks, along with a focus on the research, development, and commercialization of improved production technologies and innovative sustainable feedstocks. Government support through policies and financial incentives is crucial in providing the framework and motivation necessary for the aviation industry to scale up SAF production and adoption effectively.
The key to greater acceptance and deployment of SAF is reduction in costs. Over the long term, that will require investment in advanced technologies to process feedstocks more efficiently at greater scale and investment in the development of sustainable and scalable feedstock options. However, in the short-term, interim support from governments and other stakeholders through policy incentives is needed. This support needs to be part of a long-term framework to give investors the confidence to make the big investments required to grow supply.
Spritju’s Role in Sustainable Aviation Fuel Production
Figure 3: SAF production cycle and Spritju’s role
Spritju significantly contributes to the SAF production cycle by ensuring that the electricity required for production is sourced from renewable energy resources. Here's how Spritju adds value:
Energy Traceability:
- With advanced Energy Matching & Audatibility Machines, powered by AI and blockchain technology, Spritju's ensures the electricity used in SAF production is verifiably sourced from renewable energy producers. This traceability is essential for maintaining the sustainability claims of SAF.
To learn more about how our Energy Matching and Auditability Engines work, visit our website.
Token Management:
- Spritju’s developed blockchain system powered with PoS - Power of Stake Consensus Function allows traceability output to be used in e-fuel generation.
- Through this function, the origin of each kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity used in the SAF production process can be tracked and verified.
- Spritju ensures that fuel producers can certify the energy they use comes from renewable sources, offering transparency and credibility.
To learn more about how Spritju’s Token Management system works, visit our website.
Consumer Transparency:
- Through its IoT Integrator Engine, Spritju connects energy traceability data to end consumers, enabling them to make informed decisions about their energy consumption. This transparency helps build trust and encourages the use of renewable energy sources in SAF production.
To learn more about how our IoT Integrator works, visit our website.
Incorporating Spritju's advanced traceability solutions makes the SAF production cycle more transparent and reliable, supporting the industry's transition to sustainable and climate-friendly aviation fuels.



